Test Infrastructure Explained: Components, Architecture, and How to Build a Scalable Setup
Learn with AI
Any (well-functioning) system is built upon a good infrastructure. This infrastructure supports all of the functions and activities of the system and allows it to perform all of its activities smoothly.
Testing is no exception. With a good test infrastructure, QA teams can speed up their testing efforts and drastically improve efficiency.
In this article, I am going to share with you the concept of test infrastructure and guide you over the process of building one so you can apply for your team.
What I'm going to cover:
- What is test infrastructure?
- Components of test infrastructure
- How-to guide to build a test infrastructure, along with best practices
What is Test Infrastructure?

Test infrastructure is the underlying systems, processes, and tools required to facilitate testing activities. Everything you need to create, manage, and execute your tests throughout the entire testing lifecycle falls under the test infrastructure.
Examples of Test Infrastructure
Let’s say a developer pushes code to GitHub → Jenkins picks it up → builds a Docker image → deploys to the staging environment → triggers Selenium UI tests and API tests → test data is loaded from a seeded QA database → results are reported in Jira and Slack.
This entire loop is made possible because the test infrastructure is set up to handle every stage from provisioning to execution to reporting.
Components of Test Infrastructure

A basic test infrastructure usually consists of the following:
- Testing framework: These are the core libraries that provide the structure and functionality for test creation and execution. For example, if you are testing a mobile application, chances are you are using Espresso (for Android apps) or XCTest (for iOS apps). They provide a structured approach to scripting, and most of the time they also come with test execution/reporting methods to support you in the later stages.
- Testing tools: Automation testing tools simplify the coding parts so that testers don’t have to do the heavy lifting, and can focus on more strategic activities.
- CI/CD pipeline: With a CI/CD pipeline, QA teams can establish a streamlined process, where the code is integrated into a shared repository, automatically compiled, tested, and deployed to staging environments. Automated testing is an integral part of this process. It ensures that the software is frequently tested, and any detected bugs are addressed as early as possible. Read more: Top 14 CI/CD Tools Every Tester Should Know.
- Test data management: QA teams need diverse and comprehensive test data to facilitate data-driven testing. This requires a separate repository where the data is properly stored, managed, maintained, and set up for future testing.
- Test case management: Similar to test data management, having a dedicated system to manage your test cases is also a highly recommended practice. Test case management starts from the very beginning stage of test planning. It functions as a blueprint for the team to base the rest of their activities on.
Best Practices For Building a Test Infrastructure
1. Use Cloud-Based Infrastructure
Cloud-based infrastructure offers flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency for test environments. Cloud providers like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud allow QA teams to quickly set up and tear down test environments as needed without worrying about physical hardware limitations.
Why it matters:
-
Easily scale environments up or down based on testing needs.
-
Access to a wide variety of tools and integrations.
-
Reduced costs compared to maintaining on-premises infrastructure.
How to implement:
-
Use cloud services to create on-demand test environments.
-
Ensure data security by configuring appropriate access controls and encryption.
Read More: What is Katalon TestCloud? How TestCloud enables better cross-browser testing?
2. Establish a Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) Pipeline
A well-structured CI/CD pipeline ensures that testing is integrated seamlessly into the software development lifecycle.
Why it matters:
-
Ensures consistent, automated testing with every code change.
-
Reduces human intervention, minimizing errors.
-
Facilitates quicker feedback loops for developers.
How to implement:
-
Choose CI/CD tools like Jenkins, GitLab CI, or GitHub Actions.
-
Integrate automated tests throughout all stages of the pipeline, including unit tests, integration tests, and performance tests.
-
Regularly monitor and optimize the pipeline to avoid bottlenecks.
3. Regular Maintenance and Updates of Testing Tools
Test infrastructure must be regularly maintained to ensure the testing tools, frameworks, and environments are up to date.
Why it matters:
-
Keeps the testing process efficient and relevant to current technology standards.
-
Prevents disruptions caused by deprecated tools or outdated libraries.
-
Ensures compatibility with the latest software versions.
How to implement:
-
Schedule regular tool updates and maintenance checks.
-
Assign a dedicated team member to oversee infrastructure health.
-
Create a checklist for maintaining compatibility across different tools and environments.
4. Implement Version Control for Test Infrastructure Configurations
Using version control systems (VCS) like Git for test infrastructure configurations ensures that all changes are tracked, auditable, and easily reversible.
Why it matters:
-
Provides a single source of truth for test infrastructure configurations.
-
Facilitates collaboration among team members.
-
Helps roll back to previous configurations if issues arise.
How to implement:
-
Store test scripts, configurations, and Infrastructure as Code (IaC) templates in a VCS.
-
Use branching strategies to manage changes in infrastructure.
-
Regularly review and audit changes to maintain security and stability.
5. Automate Test Environment Provisioning
Manual setup of test environments is time-consuming and prone to errors. Automating the provisioning of test environments ensures consistency and reduces setup time, which is crucial for agile teams that need quick iterations.
Why it matters:
-
Speeds up the process of setting up test environments.
-
Reduces human error by automating repetitive tasks.
-
Ensures environments are consistent and reproducible.
How to implement:
-
Use tools like Docker and Kubernetes to create containerized test environments.
-
Automate the creation of environments using IaC tools such as Ansible or Chef.
-
Include environment setup scripts as part of the CI/CD pipeline.
Test Infrastructure in Manual Testing
The nature of manual testing does not require a lot of configuration in terms of test infrastructure. A test case management system where testers can simultaneously plan, keep track of, and record the results of their tests should suffice in this case.
A testing project with only manual tests works for a small number of test cases. However, as soon as the project scales and application complexity grows, the need for a dedicated test infrastructure arises. Here’s why:
- Manual testing is simple but highly repetitive. The same actions need to be manually executed over and over, which takes a lot of time.
- Human testers are prone to error. They can make mistakes along the way, tampering with the results. There can also be some inconsistency regarding how the test is executed.
- As the complexity of the application grows, the number of test cases to execute also grows, and it is costly to scale and maintain a huge team of only manual testers to keep up with the application’s growth.
The Trend To Upgrade Your Test Infrastructure To Support Automation
At some point, QA teams have to gradually move from manual testing to automation testing. In fact, automation testing is already the norm in the industry, and the future is “autonomous testing.” Once we reach autonomous testing, the test infrastructure is an intelligent system that can carry out all testing activities on its own, with little to no human intervention.
As of now, most QA teams are in the first to third stage in terms of autonomy, according to the Autonomous Software Testing Benchmark.
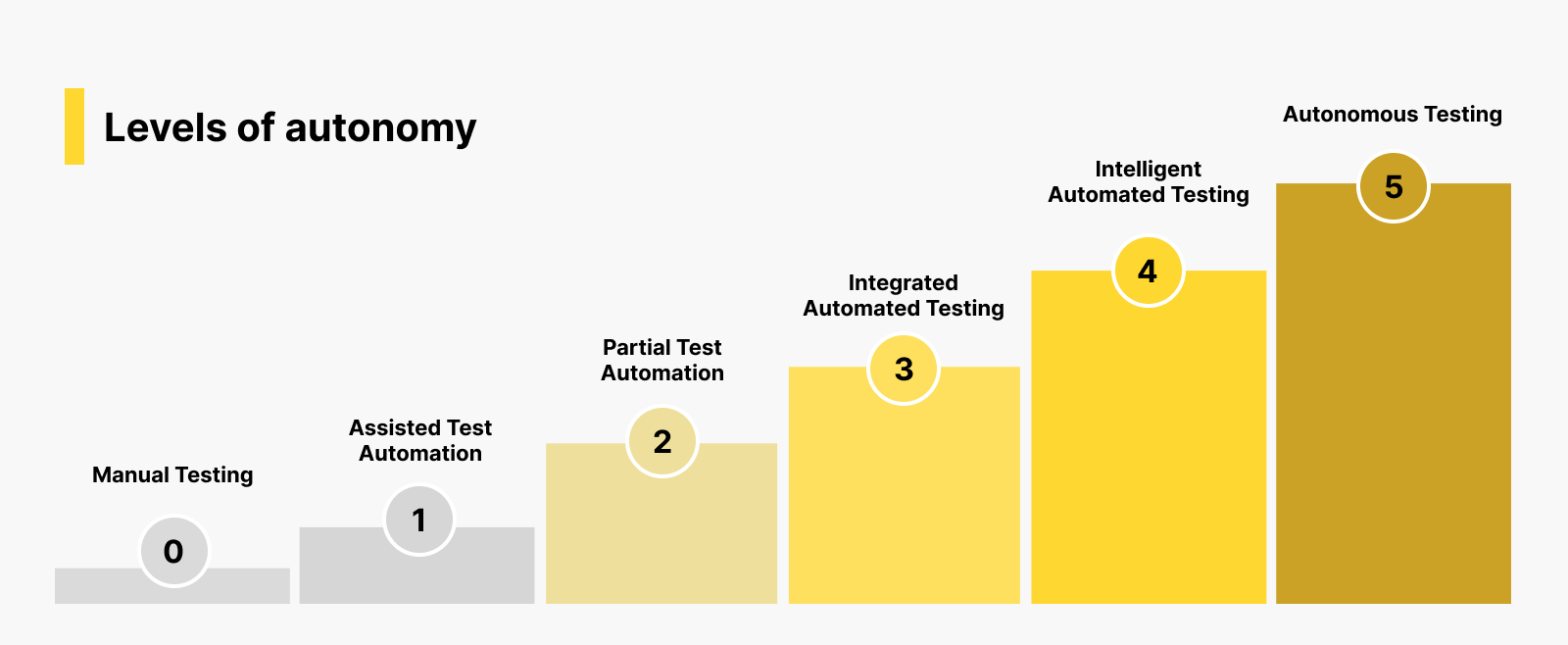
At these stages, QA teams need a test infrastructure that can support their automation efforts. This means adopting a techstack that automates and supports the automation of test cases.
How To Build Your Test Infrastructure in Automation Testing
QA teams usually have three options:
- Automate test cases with open-source testing libraries/frameworks. The goal is to create higher levels of abstraction around the core library’s functionality so that the framework is more user-friendly and versatile. QA teams also have to build their own test management, test reporting, and test maintenance features.
- Single-point automation testing tools. Here we have commercial tools that satisfy a single testing purpose (UI testing, functional testing, API testing, etc.). These tools usually come with features to support test management, reporting, as well as CI/CD integration.
- Software quality management platform. Here all types of AUT are integrated into one single testing platform, while also providing the necessary features as a complete test infrastructure in and of itself. There is no need to integrate dozens of single-point tools together. You have everything in one place.
Let’s see how you can have an entire test infrastructure ready to use in Katalon.

With Katalon, you have an entire test infrastructure built in one place. You can go through the entire testing life cycle (from planning, test creation, management, and execution, to reporting) for web, desktop, mobile, and even API, without the need to code.
Download and Witness It For Yourself
Here’s how Katalon does it:
- No-code, low-code, and full-code modes: Katalon provides testers with three test creation modes.
- No-code: Using the Record-and-Playback feature, testers can record their on-screen actions and then automate them into a test script that they can replay as many times as needed.
- Low-code: Katalon also offers a collection of Built-in Keywords, which are essentially pre-written bits of code with adjustable settings aimed at carrying out particular tasks. For instance, a keyword like “Click” manages the technical steps to find an element (like a button) and execute a click on it. Testers simply need to indicate the element they want to interact with, without needing to concern themselves with the code running in the background.
- Full-code: Testers have the option to effortlessly activate Scripting mode and independently craft their test scripts. They can seamlessly switch between the no-code and low-code modes whenever necessary. These two modes complement the full-code mode, offering the best of both approaches.
- All stages of testing are unified in one workspace: You can plan, write, and organize tests into test suites, execute them across various environments, and generate reports—all in one place. Achieving such centralization is more challenging with Appium, as it requires multiple additional integrations and significant framework development. In contrast, Katalon provides these features out of the box, making the testing process more streamlined and accessible.
- Smart reporting: After execution, you can access Katalon TestOps to get a full dashboard with charts, graphs, and diagrams to show patterns in your test results. You can zoom in/out on your test data by adjusting time frames to have a more comprehensive view.
Curious? Here's a demo:
|
FAQs on Test Infrastructure
What is test infrastructure in software testing?
Test infrastructure is the underlying setup of systems, processes, tools, and environments needed to create, manage, and execute tests across the entire testing lifecycle, with the goal of efficiency, scalability, and reliability.
What are the core components of a basic test infrastructure?
Common components include a testing framework, testing tools, a CI/CD pipeline, test data management, and test case management (so teams can plan, run, and track tests end-to-end).
Can you explain a real example of test infrastructure in action?
A typical flow is: code pushed to GitHub → CI tool (e.g., Jenkins) builds (e.g., Docker) → deploys to staging → triggers UI/API tests (e.g., Selenium) → loads seeded QA data → reports results to tools like Jira/Slack.
What best practices help teams build scalable test infrastructure?
The article emphasizes: use cloud infrastructure, embed testing in CI/CD, regularly maintain/update tools, version-control infra configs (Git/IaC), and automate environment provisioning (e.g., Docker/Kubernetes + IaC tools).
How does test infrastructure differ for manual vs. automation testing, and what are common build options?
Manual testing can be lighter (often test case management is enough), but scaling pushes teams toward automation. For automation infrastructure, teams usually choose between open-source frameworks (build lots yourself), single-point commercial tools, or an all-in-one software quality management platform (the article positions Katalon as providing a unified workspace, multiple authoring modes, and reporting via TestOps).
