Effective Mobile Testing Strategy To Help Streamline Testing
Learn with AI

Today's smartphones are far more than a device used for calling or texting. With several apps installed, they can become your virtual personal assistant.
In a mobile-centric digital world, delivering an immersive mobile experience with consistent quality is a real challenge, where QA strategy plays a critical role.
Carefully planning out what should be executed is the first important step to delivering fully-functional applications, gaining high retention rates and achieving business goals.
From choosing between testing devices to going agile, read on to find out what’s behind the scene of a solid app testing strategy.
What is Mobile Application Testing?
Mobile application testing refers to the verification of an app’s functionality, usability, and performance to ensure it works properly once in the hands of end users.
In the digital transformation era, mobile apps not only bring customers extensive utilities but also open up opportunities for organizations to leverage their business prospects.
According to Globe Newswire, the global mobile application market is expected to expand at a CAGR of 13.4% and reach USD 565.40 billion by 2030. Developing a flawless mobile experience enables companies to satisfy customers, increase engagement, and take advantage of the potential market landscape.
On the way to becoming digital-ready, mobile testing is a crucial component that can't be ignored. Imagine a health tracking app with inaccurate metrics display or a fintech app failing to protect users' data. The impact of such malfunctions will be felt on both individual and enterprise levels.
Therefore, building a robust mobile testing strategy is of paramount importance, especially when mobile apps are becoming more ubiquitous than ever.
Read more: How mobile apps fuel the digital transformation of businesses
Emulators/Simulators vs Real Devices
There are 2 main environments for mobile app testing: virtual testing devices (emulator and simulator) and real testing devices.
1. Emulators/Simulator
A virtual testing device is a software run on computers to mimic the features and behaviors of a particular smartphone.
Two main types of virtual devices are emulators and simulators. While an emulator imitates both the hardware and software of the target device, a simulator only replicates software by mimicking its various configurations in the real environment.
2. Real Devices
On the other hand, real devices are actual consumer handsets on which the software is run in a real-world production environment.
This table shows each method’s pros and cons.
|
Criteria |
Real Devices |
Emulators/Simulators |
|
Reliability |
Testing performed under real user conditions provides more reliable outcomes and better UX/UI validation. |
Compromised and less accurate results as virtual devices only reimplement the original software. |
|
Accessibility |
Building a device farm for every smartphone model takes up a lot of resources. |
Virtual devices allow testing mobile apps across various platforms and OS versions. |
|
Suitability for debugging |
Hard to connect with IDE, leading to difficulties in debugging and logging defects. |
Enable easier debugging and accelerate the testing process. |
|
Application |
Suitable for performance testing, usability testing, and regression testing in the final stage before app release. |
Ideal for the beginning stage of code development that requires continuous iteration and testing cycles. |
3. Choose the Appropriate Testing Environment

To ensure that software testing methods are effective, selecting the best testing environment is crucial. Best practices for choosing the most suitable device are:
- Define specific objectives: Understand clearly what you want to achieve: Emulators and simulators are useful for early-stage testing due to their low cost, while real devices are inevitable for accurate real-world testing.
- Analyze system requirements: Carefully examine the software's requirements to identify the components needed for testing, such as hardware, software, and network configurations.
- Examine the target audience and the devices they use: Emulators/simulators can cover a variety of devices, but real devices can ensure accurate testing on specific models and configurations that users have.
- Consider test automation: Apply test automation for repetitive tasks. Emulators/simulators can be more efficient for automation, yet real devices are valuable for manual testing and user experience evaluation.
The chosen approach is not necessarily restricted to either virtual or real devices. A combination of 2 environments can deliver the best of both worlds: the ability to test under real-use scenarios while still keeping it cost-saving and scalable. Particularly for apps targeting multiple platforms (iOS, Android, etc.), combining virtual and real devices can enhance efficiency and accuracy.
Types of Mobile Applications
Another aspect that requires clear understanding is the differences between types of mobile apps. Regarding the technology the code is based on, mobile applications are categorized into three types:
1. Native Applications
Native applications are built specifically for one platform or operating system, may it be iOS, Android, or Windows. It means that a native app developed for iOS can’t be accessed or function efficiently on Android devices. While this clear focus helps optimize the app performance, teams have to double the work for each different platform.
2. Hybrid Applications
Hybrid apps are developed upon the source code of web technologies (HTML, CSS, and JavaScript) hidden under the appearance of native apps. In other words, they are web apps at the core but have the interface and user experience of native ones.
Written in a single codebase, hybrid apps enable a streamlined and more Agile development life cycle. However, it might compromise the app’s capabilities and end-user experience.
3. Responsive Web Apps
These are basically websites that are adapted to be more friendly for mobile view and usage. This approach guarantees that a web browser functions as properly on desktops as it does on mobile devices, tablets, or TVs. For example, https://mbasic.facebook.com has the subdomain “mbasic” in front of the domain name “facebook”, demonstrating it is a web dedicated only to mobiles.

This dedicated web version is designed specifically for mobile users, ensuring that they still receive the full, or at least most of, the experience of the desktop version. For example, many elements are rearranged to suit the screen resolution, and many mouse-specific interactions (clicking/scrolling) are changed to mobile-specific interactions (tapping/swiping).
Responsive web apps grant users cross-platform accessibility but cannot work without internet connection or be downloaded through an app store.

Differences Between Test Plan and Test Strategy
Test plans and test strategies are both essential components of effective mobile testing; however, they serve different roles and strive for distinct objectives.
The following table demonstrates the differences between a test plan and a test strategy:
|
Criteria |
Test Plan |
Test Strategy |
|
Role |
A test plan is a detailed document that outlines specific test cases, procedures, and execution details. |
A test strategy is a higher-level document that defines the broader approach and methodologies for a software testing project. |
|
Scope |
Thoroughly defines every testing activity: Provide a roadmap for the testing team about what, how, and the order of testing. |
Addresses higher-level aspects of testing techniques and strategies: the overall testing objectives, the test environment, risk assessment, and the selection of testing tools. |
|
Objectives |
Ensure that each feature and functionality of the software is thoroughly tested to meet specific quality standards: defining the test scope, resources, and responsibilities. |
Provide a strategic direction for the testing procedure: aligning testing activities with project goals to ensure the testing process is efficient and effective. |
Overall, a test strategy offers a broad framework and principles for the entire testing process, whereas a test plan focuses on the specifics of how various components or features should be tested. Collaboratively, they ensure a thorough and organized approach to software testing as test strategy directs the development of specific test plans.
Mobile Application Testing: Risks and Challenges
The booming of smartphones offers a wide range of models that meet any kind of customer demand at any price point. However, it puts huge pressure on the backend teams to deliver application quality across devices. Below are the major challenges that need to be factored in and addressed when planning your mobile testing strategy.
1. Device fragmentation
With 6.4 billion mobile users worldwide, device fragmentation poses a top ordeal for development and quality teams. Fragmentation is the total combination of different devices, platforms, browsers, operating systems, and more. As of the writing of this article, these are the combinations of devices - OS - browsers that testers have to take into consideration when developing their mobile testing strategy:
- Devices: smartphones, tablets of a variety of brands
- Operating systems: iOS, Android, Blackberry OS, Windows OS, etc.
- Browser engines powering browsers: Blink, WebKit, NetFront, Gecko, EdgeHTML, etc.
- Browsers: Google Chrome, Safari, Firefox, Microsoft Edge, Opera, etc.
Considering such a wide range of variants, testing would require much more than a single, standard framework to ensure the app’s compatibility on most devices. Creating a physical hub of popular handsets is one way to overcome this hurdle, but such infrastructure calls for extensive investment and limited scalability.
This is where a testing solution such as Katalon can be of great help. As automated tests can be executed on any available browser, version, or OS, teams can achieve more device coverage and testing efficiency.
Either way, it’s always important to run tests on multiple environments. Limiting the number of testing devices means diminishing your user base and curbing the company's potential growth.
2. Updated device models
Besides the daunting number of devices available, challenges also arise from new technologies introduced during the application life cycle. When iPhone 14 launches with its “dynamic island”, app developers must modify their apps to ensure seamless interaction with the new interface.
Updating an app and testing new configurations accordingly is an ongoing practice rather than a set-and-done task.
3. Security
Poorly encrypted apps are highly vulnerable to security breaches. Ensuring apps’ absolute security wall over the users’ data remains one of the top priorities to avoid risks of personal information leaks or hacker attacks.
Strong encryption and extensive testing are essential to protect apps from security issues.
4. Too many app testing tools
One can be spoiled for choice when it comes to the tool selection process. While there are tools for various testing needs, subscribing to single-point solutions can make the system fragmented, leaving holes for data risks and poor performance.
In this case, Katalon - a thorough quality management platform, can be the solution to your mobile testing. With cross-environment execution, optimal cross-functional testing, and other capabilities, Katalon helps app providers to streamline mobile testing and deliver high-quality products.
Different Types of Effective Mobile App Testing Strategies
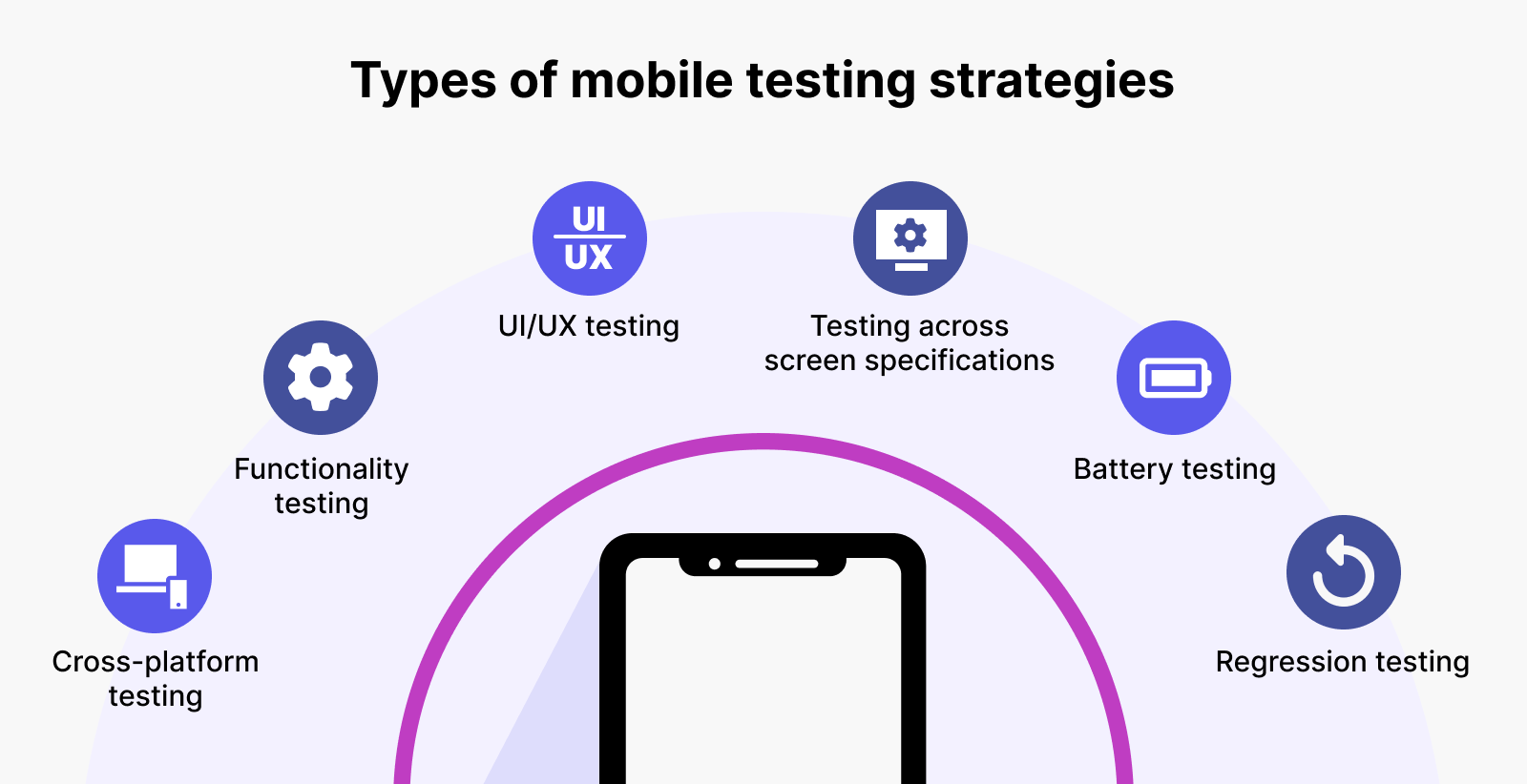
The above problems can be tackled with a well-thought mobile application testing strategy, which should include the following items:
1. Cross-platform testing
Customers expect apps to function uniformly regardless of the OS version they are on. While iOs and Android are the two dominant mobile OSs on the market, their differences in programming languages ask teams to adapt the testing approach to deliver cross-platform compatible apps.
2. Functionality testing
Did you know that 53% of mobile app users uninstall an app with severe issues like crashes, freezes, or errors? Functional testing ensures every app feature works properly, leaving little to no room for broken functionalities to achieve higher retention rates.
Functional testing is applied to test UI elements, screen adaptation, core structures, and functions of the app. It also tests the installation and update processes, localization settings, compatibility, and accessibility of the application.
3. UI and UX testing
Frictionless UX design could potentially raise customer conversion rates up to 400%.
An application's success boils down to its user experience - how the end users perceive and interact with the product. Usability testing checks if the app is simple to navigate and user-friendly. The final goal is to bring a smooth and intuitive mobile experience.
4. Testing across different screen dimensions and specifications
When testing a mobile app, it is utterly crucial to ensure it looks and functions well on various screen sizes and resolutions, which involves testing on devices with multiple dimensions and specifications, including phones and tablets.
Indeed, testers are required to verify that the app's layout is responsive, text remains legible, and all features work smoothly, regardless of the screen size, ensuring a consistent user experience across a wide range of devices, which is vital for app success.
5. Battery testing
It is indubitable that battery life plays a crucial role for mobile users and an effective mobile app testing would definitely include assessing its impact on a device's battery.
In this case, testers monitor the power consumption during different app activities, including browsing, streaming, or gaming. By identifying power-hungry elements or inefficiencies, the QA team can optimize the app to minimize battery drain and create a more battery-friendly app, enhancing user satisfaction.
6. Regression testing after each update
When any mobile app receives updates, it should seamlessly transition from the older version to the new one. Hence, testers must simulate various upgrade scenarios, including users with different versions of the app and different settings, to ensure that data migration, user settings, and app functionality remain unchanged during upgrades.
By thoroughly testing these scenarios, testers can prevent user data loss and maintain a smooth user experience when applying updates.
5 Strategies To Streamline Mobile App Testing For Agile Projects
1. Early testing
One of the main philosophies of agile development is to test early and fail fast. In contrast with the traditional waterfall approach, testing in agile is shifted left and performed in parallel with the development process.
If a bug goes unnoticed during development, the following domino effect of failures can raise the fixing cost exponentially. Testing done early is to prevent any minor bug from spiraling into a critical error, keep the expense within the budget and deliver apps promptly according to the timeline.
Agile testing methodology helps teams achieve regular feedback loops, a continuous delivery pipeline, and confidence about quality in every iteration.
2. Establish an alignment between the dev and testing team
Facilitating such a flexible approach needs well-oiled communication and collaboration among members.
It's hard to avoid silos or miscommunication when information is fragmented and not updated in real-time. Without streamlined communication, the entire project is at risk of failure.
Having everyone on the same page is critical and should be prioritized before anything else in your strategy.
3. Infrastructure readiness
Coming right after the human resource is the preparation of the mobile testing environment.
May it be emulators/simulators or physical devices, the selected solution should meet specific requirements, such as an easy learning curve, suitable testing features, or native integrations.
Examining these criteria when selecting a testing tool helps guarantee an efficient and stable testing process.
4. Exploratory testing
It is about exploring various features of a particular application without having a test plan or a feature request. Exploratory testing is typically performed by skilled testers who can pinpoint defects outside the scope of the planned test using their previous experience.
Exploratory testing helps your strategy to be more comprehensive and focused for higher test coverage.
5. Automated mobile app testing
During the life cycle of a mobile app, many functionalities will be added later on, which may cause new bugs. Identifying such bugs can be done automatically to reduce the repetitive manual efforts while increasing the depth and scope of testing.
A high level of automation is essential to detect regression bugs and allow teams to ship quality applications.
An effective mobile app testing strategy should go hand in hand with test automation frameworks/tools that are powerful and easy to scale.
Considering the vast number of tools available in the market, one can get lost when looking for the right one. Here we list the top 10 automated mobile app testing tools to help you choose your best fit.
|
FAQs
What is mobile application testing?
It’s the verification of an app’s functionality, usability, and performance to ensure it works properly for end users.
What’s the difference between an emulator and a simulator in mobile testing?
An emulator imitates both hardware and software of the target device, while a simulator replicates software and mimics configurations in a real environment.
When should you use emulators/simulators vs real devices?
Emulators/simulators are ideal early in development for continuous iteration and easier debugging; real devices are suited for performance, usability, and final-stage regression testing under real user conditions.
What are the three types of mobile applications described?
Native apps (platform-specific), hybrid apps (web tech under a native shell, single codebase), and responsive web apps (mobile-friendly websites accessed via a browser).
What are some major risks and challenges in mobile testing strategy?
The content highlights device fragmentation, updated device models, security vulnerabilities (need strong encryption and extensive testing), and the problem of having too many single-point testing tools.


