API Regression Testing: How to Automate, Validate, and Prevent Breaking Changes
Learn with AI
API is the backbone of many software architecture. However, it is also one of the major points of technical conflict. When a major code update happens, it is really important to check on these APIs to ensure that those code modifications did not inadvertently break existing functionality.
This is why API regression testing should be considered in your regression test planning.
What is API regression testing?
API regression testing is the process of re-running tests on an application's APIs to ensure that recent code changes have not introduced new bugs or broken existing functionality.
It ensures that the core contract of an API remains stable over time, even as internal implementations evolve.
✍️ Learn More: A Basic Guide To Regression Testing
What to consider when regression testing APIs
- When testing an API, start by verifying the status codes. Every request should return the correct HTTP response, like 200 for success, 400 for bad requests, or 401 for unauthorized access. This is a basic but essential check.
- Next, validate the response schema and data. Use the API's specification (such as Swagger/OpenAPI) to ensure the returned structure matches what's expected: field names, data types, required vs. optional fields, and so on. Schema mismatches are common sources of bugs.
- Cover a variety of test scenarios, not just the "happy path." Test valid and invalid inputs, missing parameters, boundary values (e.g. max, min, max+1), and wrong data types. Send unexpected values and see how the API responds.
- Check for authentication and authorization. Test endpoints with and without tokens, and verify access controls for users with different permission levels. A user with no permissions should not access restricted data.
- Perform CRUD flow tests (Create, Read, Update, Delete) to ensure data consistency. For example, create an object, fetch it, update it, then delete it and confirm each step returns the correct data and response.
- Include error handling checks. Send malformed payloads or violate business rules, and ensure the API returns the right error codes and helpful error messages.
- Don’t forget performance. Monitor response times and consider running load or stress tests on critical endpoints to ensure stability under traffic.
- Validate data integrity after updates. If the API writes to a database or affects other systems, verify that the changes are properly reflected everywhere.
- Lastly, test for security issues. Check that sensitive data isn’t exposed, simulate injection attacks, and confirm proper validation on both client and server sides.
📚 Resources: Top API Test Cases You Should Know
How to automate API regression testing
API regression testing is most effective when integrated early into the development workflow, ideally at the pull request (PR) level. Running your regression suite at this stage helps catch issues before they make it into staging or production, shortens the feedback loop, and saves developers from creating follow-up fixes or hotfixes.
To do this reliably, your tests should spin up an isolated instance of the System Under Test and mock any external dependencies. This ensures that your tests are validating application logic without being affected by flaky environments or unavailable services.
Once merged, you can run a broader end-to-end regression suite in a real or production-like environment, using real APIs and infrastructure. This verifies system-wide stability and ensures that integrated services are working as expected.
Top tools for automated API regression testing
1. Katalon

Katalon provides an all-in-one testing solution for any type of test project. It supports web, mobile, API, and desktop application testing. For API testing in particular, Katalon supports you throughout the entire API testing lifecycle, from test planning, test creation, to test execution and test reporting for many types of API requests on multiple environments.
- API Test Creation: Katalon comes with many codeless test authoring capabilities, including Built-in Keywords, which are readily available code snippets that you can drag and drop to build a full test, and Record-and-Playback, which allows you to record the sequence of your activities, auto-capture test objects, and turn them into a test script. This helps tremendously in creating even the more complex API narratives.
- API Test Organization: all test objects captured are organized in a repository with clear hierarchy. These objects can be reused across a wide variety of environment and scenarios. Via Postman and repo integration, you can easily reuse existing API assets, or consolidate resources for team collaboration.
- API Test Execution: Katalon gives you access to many web and mobile environments to run your tests on. You can choose to run tests on cloud with Katalon TestCloud or run on your local environment through the CLI with Katalon Runtime Engine, which has many AI-powered features to support API test maintenance.
- API Test Analysis: after test runs, Katalon generates detailed reports with relevant metrics for you to monitor your efficiency and make data-driven decision.
- API Test Planning: integrate with Slack, Microsoft Teams, JIRA, and many collaboration platform for enhanced communication and visibility across teams
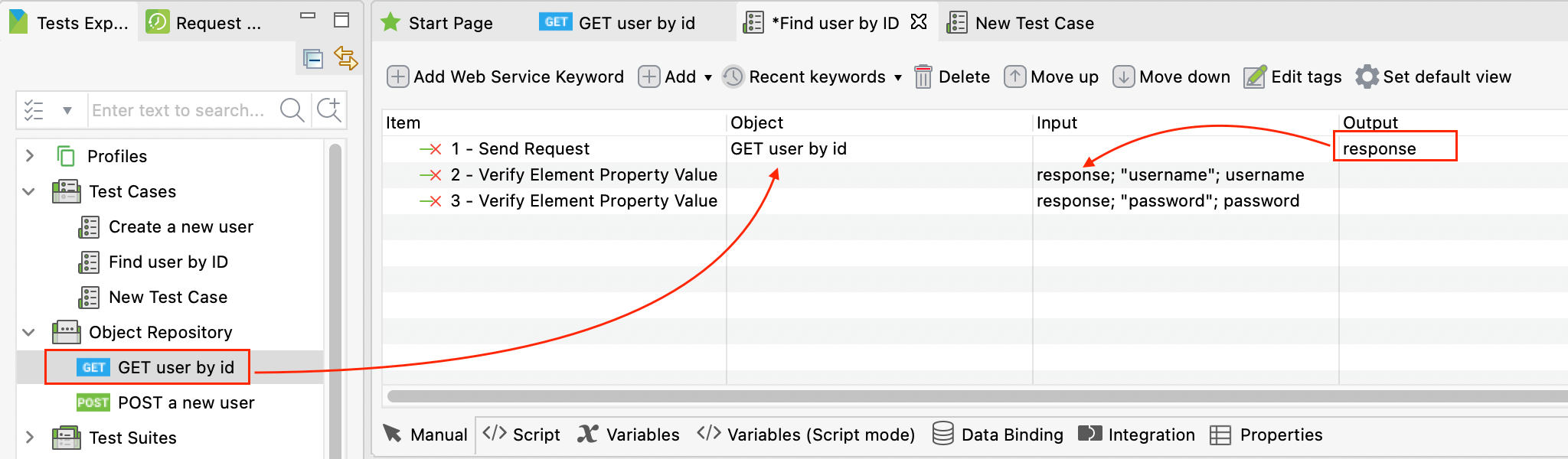
For example, after creating a test project in Katalon Studio, you can click on “Add Web Service Keyword” to generate test steps, which are “Send Request” and Verify Element Property Value" here, then simply drag-and-drop objects from the Object Repository on the left sidebar to define what those test steps include. Instead of writing code, you have constructed a full API test from scratch in seconds.
The tool is constantly adding in test integration features and improving over time, allowing users to scale up testing projects with confidence. Beside that, it also has a scripting mode for experienced testers, reducing the time it takes for API test creation. It is the perfect Postman alternative for teams of all scale and expertise.
2. Bruno

Bruno emerges as a fast and innovative open-source API client aimed at challenging the norms set by established tools like Postman and Insomnia.
What sets Bruno apart is its unique approach of storing API collections directly on your local filesystem, using a plain text markup language called Bru for managing API requests. This approach not only simplifies storage and version control but also enhances accessibility and transparency in managing API documentation and tests.
Unlike cloud-based tools, Bruno operates offline-only, ensuring maximum data privacy by keeping all collections securely on the user's device. This commitment to data security is a key feature for users who prioritize privacy and control over their API testing environments.
Features:
- Filesystem storage for API collections
- Uses plain text markup language (Bru) for API requests
- Seamless integration with Git and other version control systems
- Open-source with customization opportunities
API regression testing best practices
- Follow the Testing Pyramid principle. Most of your automated test coverage should be at the unit and API levels, not the UI. API-level tests are faster, cheaper to maintain, and provide better feedback granularity. GUI tests should be minimal, reserved for critical end-to-end flows, and kept small and atomic.
-
Organize tests by category: smoke, sanity, full regression. Run smoke tests on every commit, sanity suites post-merge, and full regression before releases. Use tagging or configuration flags to switch between modes without duplicating logic.
- Focus your regression suite on high-value coverage. Prioritize endpoints that are business-critical, frequently changed, exposed externally, or known to be unstable. Build test scenarios that cover valid inputs, edge cases (min, max, null, overflow), invalid types, unauthorized access, and missing fields. Include both functional and negative tests.
- Validate not just behavior, but structure. Use OpenAPI/Swagger schemas and JSON schema validation to ensure your API response formats remain consistent. Schema regressions are subtle but high-impact, especially for downstream consumers.
-
Lastly, treat documentation as a first-class input. Ensure your API specs are accurate, up to date, and cover both expected outputs and failure modes. Regression testing is exponentially harder without reliable reference contracts.
|
FAQs on API Regression Testing
What is API regression testing?
It’s re-running tests on an application’s APIs to ensure recent code changes didn’t introduce bugs or break existing functionality and that the API contract remains stable over time.
What should you verify first when regression testing an API?
Start with HTTP status codes (e.g., 200, 400, 401), then validate response schema and data against the API specification (like Swagger/OpenAPI).
Which scenarios should API regression tests cover beyond the “happy path”?
Valid and invalid inputs, missing parameters, boundary values, wrong data types, unauthorized access, error handling, CRUD flows, performance checks, data integrity, and security checks (including making sure sensitive data isn’t exposed).
How can you automate API regression testing effectively in the workflow?
Run regression suites early at the pull request level using isolated instances and mocked dependencies, then run broader end-to-end regression in production-like environments post-merge.
What are key best practices for API regression suites?
Follow the testing pyramid (most coverage at unit and API levels), categorize suites (smoke/sanity/full regression), prioritize high-value endpoints, and use OpenAPI/Swagger plus JSON schema validation to keep response formats consistent.

%20(9).png)
