10 Popular API Examples: A Full List
Learn with AI
Every time you use an app such as Facebook or Instagram, check the weather or send an instant message, you’re using an API.
API examples are everywhere, in the applications you use on a daily basis. APIs are basically the middlemen of apps and web services, allowing different applications to communicate with each other. They are a key aspect of our digital world and in software development.
With APIs, we are able to engage in digital experiences on our phones and computers every day. So what are APIs and some API examples? Here we will explain the concept of API in the most understandable way and provide you with 10 most popular examples of API.
In this article, you will get to learn about:
- Twitter API
- ChatGPT API
- Google Map API
- Discord API
- Github API
- Paypal API
- eCommerce API
- YouTube API
- Instagram API
- Slack API
What is an API?
Imagine the weather app is like a restaurant kitchen, and the messaging app is like a waiter.
The kitchen (weather app) makes the food (weather updates), but it doesn’t talk directly to customers.
Instead, it uses the waiter (API).
The API is the waiter. The messaging app (customer) tells the API (waiter), “I’d like the weather forecast, please.” The API takes that request to the weather app’s server (kitchen), gets the info (the food), and brings it back.
So basically: An API is a messenger that lets two apps talk to each other. One app sends a request through the API, and the other app responds with the right data.
📚 Read More: What is API Testing? A Complete Guide
How to use an API?
-
Find the API you want to use (e.g. weather, news, maps).
-
Read the API documentation to see how it works—what you can ask for and how to ask.
-
Get an API key (like a password) if it’s required for access.
-
Send a request to the API using a tool or code (like typing a special URL).
-
Receive the response the API sends back the data, usually in JSON format.
-
Use the data in your app or website to show info or take action.
Actual example of how API is used
Let's say we want to get the current weather in London using a free weather API called Open-Meteo.
- We are using a real weather service that requires an API key.
- The key is used in the URL as a query parameter: ?key=YOUR_API_KEY.
- We send a fetch() request to the API. This request asks for the current weather in London.
- The server checks if the API key is valid before responding.
- If the key is correct, it sends back a JSON object with weather info.
- We extract the temperature and print it using console.log().
- If there’s a mistake (like wrong key or city not found), we handle it in .catch().
Here's the script for the API:
// Example: Get weather info from Open-Meteo API
const city = 'London';
const url = `https://api.open-meteo.com/v1/forecast?latitude=51.5&longitude=-0.1&_weather=true`;
fetch(url)
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => {
const temperature = data.current_weather.temperature;
console.log(`The current temperature in ${city} is ${temperature}°C`);
})
.catch(error => {
console.error('Error fetching data:', error);
});
To make sure an API works properly, QA teams have to test them by running those APIs through a wide variety of real-life use cases.
Types of API
There are so many types of APIs. Below are several of them:
By use case:
- Open APIs: publicly available APIs that anyone can use to access a company’s data
- Internal APIs: APIs used within a company/organization to communicate information between internal apps
- Partner APIs: APIs designed specifically for third-party developers/partners, and are more limited in access
By protocols:
- REST API: a widely used architecture for building web services using HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE format to interact with data resources. REST APIs typically return data in JSON or XML format
- SOAP API: a messaging protocol used to exchange structured data between web services. SOAP APIs use the XML format for data exchange, and they typically require more bandwidth and processing power than REST APIs. SOAP APIs support more advanced features like transaction, security, and reliability
- GraphQL API: a query language for APIs that was developed by Facebook. GraphQL APIs allow developers to retrieve only the data they need, using a single query. This can result in more efficient data retrieval and reduced network traffic. Learn more about GraphQL testing.
- Webhook API: a way to send real-time data from one application to another. Webhook APIs use a simple HTTP POST request to send data to a URL specified by the recipient application. The recipient application can then take action on the data in real-time. Webhook APIs are often used for event-driven applications, such as chatbots or notification systems.
10 API Examples of Popular Apps
1. Twitter API
Twitter offers a wide variety of APIs that developers can use to build applications that interact with Twitter. As one of the most popular social media platforms, Twitter is a great destination for businesses wanting to advertise their products and services.
Twitter's Ads API provides businesses with a way to create and manage their advertising campaigns on the Twitter platform.
For example, social media marketing management tools like Buffer allows users to schedule their Twitter marketing calendar, and they must use Twitter APIs to extract analytics from Twitter for their users. Below is the Buffer dashboard with important Twitter metrics such as tweets, replies, retweets, clicks, and more.

Source: Backlinko
Another interesting API is the Twitter Direct Message API.
With the Twitter Direct Message API, developers can create chatbots that can automatically respond to DMs, providing information, answering questions, or carrying out other tasks.
For example, a company can use a chatbot to provide customer support through Twitter DMs, allowing users to quickly get help with their questions or issues.
2. ChatGPT API
The ChatGPT API is a cloud-based service from OpenAI that allows developers to integrate the power of ChatGPT into their own apps, websites, or software systems.
It works like any other API:
-
You send a request to OpenAI’s servers with a message or instruction.
-
OpenAI’s model processes it and returns a response (a reply, summary, suggestion, etc.).
-
You handle that response in your app however you want.
It uses HTTP and returns data in JSON format.
Here are some real-world examples:
-
Customer Support Chatbot: Create a chatbot that handles customer questions on a website using ChatGPT.
-
Email/Message Drafting: Build a tool that helps users generate or rewrite emails.
-
Auto-Generated Reports & Summaries: Pull in user data or meeting notes and summarize them with GPT.
-
Content Generation in CMS/Blog Tools: Use ChatGPT to draft blog intros, product descriptions, or FAQs.
3. Google Map API
The Google Maps API is a tool that allows developers to place interactive maps inside websites or apps. Instead of just linking to Google Maps, this API lets the map appear right on the page, fully customizable.
To use it, developers first need to get an API key from Google. This key identifies who's using the service and helps prevent abuse.
With the Google Map API, you can:
-
Embed a map directly into your site or app
-
Add markers to highlight specific locations (e.g. stores, delivery spots)
-
Customize how the map looks (style, colors, zoom level)
-
Let users click on markers to view more information (using info windows)
-
Display routes, directions, or draw shapes and overlays on the map
For example, here is an Address Verification window at a local pizza shop. As you type in your address and click Find Me, the address will be sent to Google Map via the Google Map API. Google Map will return the exact location for the pizza shop so that the delivery driver knows where to bring the pizzas to.

4. Discord API

Discord is a free app where people can chat using text, voice, or video. It’s popular with gamers but also used by many other communities. People talk in servers, which are like group chat rooms for specific topics.
The Discord API lets developers connect to Discord using code. It allows them to make bots or create tools that work with Discord.
One way to use the Discord API is through something called a REST API. This means you send a request to Discord’s server (like asking a question), and it sends back data (like an answer).
Here are some of the cool things you can do with it:
-
Get a user’s profile picture or username
-
Send messages with a bot
-
Create channels or manage roles
-
Use Discord data inside another app or website
5. GitHub API

GitHub is a website where people store and share code. It’s used by developers to work on projects together, track changes, and manage code versions. Each project lives in a “repository,” which is like a folder for code and files.
The GitHub API lets developers connect to GitHub using code. It allows them to build tools or apps that can read or change things on GitHub automatically.
One way to use the GitHub API is through something called a REST API. This means you send a request to GitHub’s server (like asking a question), and it sends back data (like an answer).
Here are some of the useful things you can do with it:
- Get a list of repositories for a user or organization
- Create a new issue or comment on one
- Check if someone has starred a repo
- Pull data about commits, branches, or contributors
- Use GitHub data inside another app or dashboard
6. PayPal API

PayPal is one of the most popular ways to send and receive money online. People use it to shop, pay bills, or transfer money safely. You’ll often see a PayPal Checkout button on online stores.
The PayPal API lets developers connect to PayPal using code. This makes it easy to add things like “Pay with PayPal” buttons on a website or app.
When a customer clicks the button, they’re taken to PayPal to finish the payment. Their credit card info is already saved in PayPal and never shared directly with the website. That makes it more secure.
Here are some things you can do with it:
- Add a PayPal Checkout button to your site
- Charge a customer’s PayPal account
- Set up automatic payment subscriptions
- Send refunds through code
- Get order status and transaction history
Below is a code example of how PayPal's API is used to add a checkout button and process a basic payment on a website:
<script src="https://www.paypal.com/sdk/js?client-id=sb-example1234567890¤cy=USD"></script>
<div id="paypal-button-container"></div>
<script>
paypal.Buttons({
createOrder: function(data, actions) {
return actions.order.create({
purchase_units: [{
amount: {
value: '19.99' // Sample product price
},
description: 'Sample Product: Retro T-shirt'
}]
});
},
onApprove: function(data, actions) {
return actions.order.capture().then(function(details) {
alert('Payment completed by ' + details.payer.name.given_name + '!');
});
},
onError: function(err) {
console.error('An error occurred:', err);
}
}).render('#paypal-button-container');
</script>
What it does is:
-
It loads the PayPal SDK from PayPal’s servers using a sample client ID (you’d replace it with your real one).
-
It creates a button on the page that says something like “Pay with PayPal.”
-
When someone clicks the button:
-
It creates an order for a sample product that costs $19.99.
-
It takes the user to PayPal so they can log in and approve the payment.
-
-
Once the user confirms payment, it captures the money and shows an alert like "Payment completed by [your name]!".
7. eCommerce API
Shopify is a platform that helps businesses build and run their online stores. It’s easy to use, and most features work right out of the box. But sometimes, businesses need more advanced or custom tools, and that’s where the Shopify API becomes useful.
The Shopify API lets developers connect to a store using code. They can build custom features, link Shopify with other apps, or automate tasks like managing products or tracking orders.
Here are a few examples of what the Shopify API can do:
-
Build a custom storefront that looks and works differently than the default Shopify theme
-
Connect Shopify to an external inventory system so stock levels update automatically
-
Add a custom payment method if the business uses a provider Shopify doesn’t support
-
Automate shipping label creation or order tracking with a delivery service
-
Sync products, prices, and orders between Shopify and a company’s internal system
With the API, Shopify becomes much more flexible, allowing developers to build tailored solutions for almost any kind of store.
8. YouTube API
YouTube provides an API that lets developers interact with videos, playlists, and channels in powerful ways. One of the most common uses is to embed YouTube videos directly into apps or websites. For example, a fitness app could display workout videos, or a learning platform could embed tutorials next to each lesson.
The API lets you customize how the video player looks and works:
-
Set the size and aspect ratio of the video player
-
Control playback options like start time or quality
-
Turn on or off video suggestions or captions
-
Match the player's appearance to your app's design
In addition to embedding, the YouTube API allows developers to access detailed video and channel data. This includes:
-
View counts, likes, and comments
-
Playlist and channel metadata
-
Subscriber stats and video tags
9. Instagram API

The Instagram API is similar to the Twitter API in that it lets developers and businesses extend what Instagram can do beyond its regular app. It’s especially useful for shop owners and brands who want to connect their Instagram content with their online stores.
For example, a store owner can use the Instagram API to display their latest Instagram posts directly on their website. This gives visitors a more complete view of the brand, showing real-time content, likes, and comments, all without having to leave the site.
The API also supports shopping features. Businesses can let users buy products directly through Instagram. When someone places an order on Instagram, the API sends that order data to the business’s website or backend system so it can be processed and fulfilled normally.
Common ways the Instagram API is used:
-
Show a live Instagram feed on a product or homepage
-
Sync post data (captions, likes, comments) to an external site
-
Handle in-app purchases and pass order info to the main store backend
-
Track engagement stats for analytics or reporting
In short, the Instagram API connects social content with eCommerce workflows, helping businesses create a more seamless shopping and engagement experience across platforms.
10. Slack API

The Slack API lets developers build tools and automations that connect directly with Slack, making it more powerful than just a messaging app. It’s often used by companies to automate workflows, send alerts, or connect Slack to other apps like CRMs, issue trackers, or internal dashboards.
For example, a developer could use the Slack API to post a message in a channel every time someone submits a form on a website. Or a sales team might get automatic Slack updates whenever a new lead is added to their CRM.
Slack bots are another popular use. With the API, you can create a bot that can reply to questions, send reminders, or even take action like assigning a task or starting a Zoom meeting right inside Slack.
What is API Testing?
APIs help apps talk to each other, but sometimes they break or return the wrong data. This can cause serious problems, like missing or corrupted information. That’s why developers need to test APIs to make sure they work correctly.
If you're preparing for a software job interview, knowing how to test APIs is important. Here's a simple guide to API testing:
-
Find the API endpoints: These are the URLs your app uses to talk to the API.
-
Know the API method and parameters: Methods include GET (read), POST (create), PUT (update), and DELETE. You also need to know what inputs the API needs—like query parameters, headers, or body data.
-
Write test cases: Cover different situations: valid input, invalid input, and edge cases. You can test with tools like Selenium (using Java) or easier tools like Katalon (low-code).
-
Set up your test environment: Make sure the API and your test tools are ready to run.
-
Run the tests and check results: Look at the responses and make sure the API works as expected.
How to use Katalon for API testing?

Katalon is an API automation testing tool that also supports web UI automation testing and mobile testing. Here's how Katalon helps:
- API test creation: You can send all types of API requests and configuring headers, query params, request bodies, authentication tokens, etc. without manually coding them. If you want full control, switch to coding mode and write one with Java/Groovy. Data-driven testing and BDD testing is also supported.
- API test management: You can save collections of API requests as test suites or test collections for better management. These suites can then be run on schedule or by trigger in the CI/CD pipeline.
- API test execution: in Katalon TestOps, you can manage test cases, schedule test runs, then view dashboard of test results. You can also run tests in the CLI.
- API Test Planning: integrate with Slack, Microsoft Teams, JIRA, and many collaboration platform for enhanced communication and visibility across teams
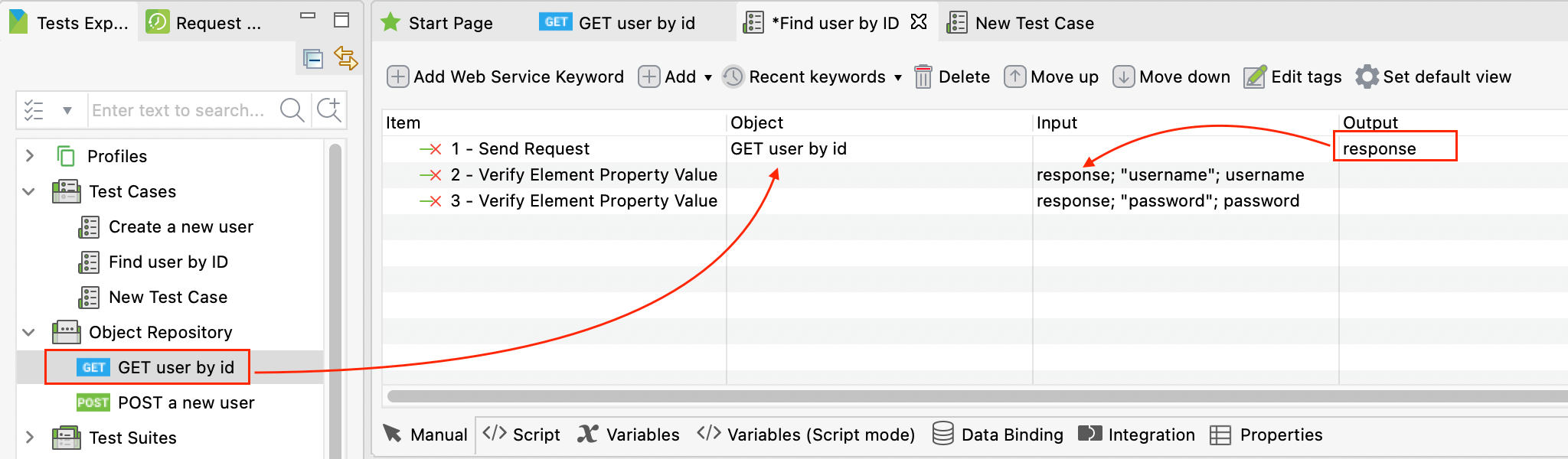
For example, after creating a test project in Katalon Studio, you can click on “Add Web Service Keyword” to generate test steps, which are “Send Request” and Verify Element Property Value" here, then simply drag-and-drop objects from the Object Repository on the left sidebar to define what those test steps include. Instead of writing code, you have constructed a full API test from scratch in seconds.
FAQs on API
1. What is the difference between REST and SOAP APIs?
REST APIs are lightweight and use standard HTTP methods (GET, POST, etc.), making them more flexible and widely adopted. SOAP APIs follow a strict protocol and XML format, offering more robust security features but at the cost of complexity and overhead.
2. How do APIs handle rate limiting?
Rate limiting controls the number of API requests a client can make in a given timeframe. It prevents abuse and overloading by issuing HTTP status codes (e.g., 429 Too Many Requests) when limits are exceeded.
3. What is API versioning, and why is it important?
API versioning manages changes in an API without disrupting existing clients. It allows developers to introduce new features or improvements while maintaining compatibility for older versions.
4. What is an API gateway?
An API gateway acts as a single entry point for client requests, handling tasks like authentication, rate limiting, routing, and caching. It simplifies API management and enhances security.
5. How do APIs ensure security?
APIs use techniques like OAuth2, API keys, HTTPS, rate limiting, and IP whitelisting to secure data and restrict unauthorized access.
6. What is an idempotent API call?
An idempotent API call produces the same result regardless of how many times it is executed. For example, an HTTP PUT request to update a resource remains idempotent, as it updates the resource to the same state even if called repeatedly.
7. How does caching improve API performance?
Caching stores responses for frequently accessed requests, reducing server load and improving response times. Techniques like HTTP caching headers (e.g., Cache-Control) and tools like Redis are commonly used.
8. What is the difference between synchronous and asynchronous APIs?
Synchronous APIs require the client to wait for the server's response before proceeding, while asynchronous APIs allow the client to continue processing other tasks and handle the response later.
9. What are webhooks, and how are they different from APIs?
Webhooks are event-driven callbacks triggered by specific actions, sending data to a client in real time. Unlike APIs, which require client requests, webhooks push updates automatically.
10. How are APIs tested?
API testing includes validating endpoints, response codes, performance, and security. Tools like Postman, SoapUI, and automated scripts ensure APIs function as expected under various conditions.
|


